Introduction to Stacks
Introduction to Stacks
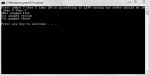
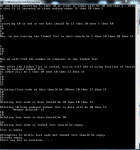
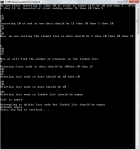
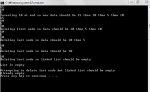
In this tutorial, you will 1. Learn the concept of stacks. 2. Be given practical examples of LIFO 3. Learn what the types of implementation of stack are? 4. learn the array based implementation of stacks. What is the concept of stacks? The concept of stacks is very simple. It is that if you insert an element in a stack, it always occupies top position and when you remove element, the element at top is always removed. i.e. the element inserted last is removed first. Another name given to such insertion is LIFO i.e. last in first out.- Read more about Introduction to Stacks
- Log in or register to post comments
- 137 views