How to Implement Doubly Linked List Operations in Python
In this tutorial, we will learn how to program “How to Implement Doubly Linked List Operations in Python.” The objective is to implement operations for a doubly linked list. This tutorial will guide you step by step through the process of creating and managing a doubly linked list. By the end of this tutorial, you will have a solid understanding of how to implement these tasks effectively in Python, helping you strengthen your problem-solving abilities and improve your coding skills.
This topic is straightforward and easy to understand. Simply follow the instructions provided, and you will complete it with ease. The program will guide you step by step through the process of implementing linked list operations. So, let’s dive into the coding process!
Getting Started:
First you will have to download & install the Python IDLE's, here's the link for the Integrated Development And Learning Environment for Python https://www.python.org/downloads/.
Creating Main Function
This is the main function of the application. The following code will display a simple GUI in terminal console that will display program. To do this, simply copy and paste these blocks of code into the IDLE text editor.- class Node:
- def __init__(self, data):
- self.data = data
- self.next = None
- self.prev = None
- class DoublyLinkedList:
- def __init__(self):
- self.first = None
- self.last = None
- def get_node(self, index):
- current = self.first
- for i in range(index):
- if current is None:
- return None
- current = current.next
- return current
- def insert_after(self, ref_node, new_node):
- new_node.prev = ref_node
- if ref_node.next is None:
- self.last = new_node
- else:
- new_node.next = ref_node.next
- new_node.next.prev = new_node
- ref_node.next = new_node
- def insert_before(self, ref_node, new_node):
- new_node.next = ref_node
- if ref_node.prev is None:
- self.first = new_node
- else:
- new_node.prev = ref_node.prev
- new_node.prev.next = new_node
- ref_node.prev = new_node
- def insert_at_beg(self, new_node):
- if self.first is None:
- self.first = new_node
- self.last = new_node
- else:
- self.insert_before(self.first, new_node)
- def insert_at_end(self, new_node):
- if self.last is None:
- self.last = new_node
- self.first = new_node
- else:
- self.insert_after(self.last, new_node)
- def remove(self, node):
- if node.prev is None:
- self.first = node.next
- else:
- node.prev.next = node.next
- if node.next is None:
- self.last = node.prev
- else:
- node.next.prev = node.prev
- def display(self):
- current = self.first
- while current:
- print(current.data, end=' ')
- current = current.next
- print()
- # ---------------- MAIN PROGRAM ----------------
- while True:
- print("\n=============== Implement Doubly Linked List Operations ===============\n")
- a_dllist = DoublyLinkedList()
- print("Menu")
- print("insert <data> after <index>")
- print("insert <data> before <index>")
- print("insert <data> at beg")
- print("insert <data> at end")
- print("remove <index>")
- print("quit")
- while True:
- print("The list: ", end='')
- a_dllist.display()
- do = input("What would you like to do? ").split()
- if len(do) == 0:
- continue
- operation = do[0].strip().lower()
- if operation == "insert":
- try:
- data = int(do[1])
- suboperation = do[2].strip().lower()
- position = do[3].strip().lower()
- new_node = Node(data)
- if suboperation == "at":
- if position == "beg":
- a_dllist.insert_at_beg(new_node)
- elif position == "end":
- a_dllist.insert_at_end(new_node)
- else:
- print("Invalid position!")
- else:
- index = int(position)
- ref_node = a_dllist.get_node(index)
- if ref_node is None:
- print("No such index.")
- continue
- if suboperation == "after":
- a_dllist.insert_after(ref_node, new_node)
- elif suboperation == "before":
- a_dllist.insert_before(ref_node, new_node)
- else:
- print("Invalid operation!")
- except:
- print("Invalid input format for insert.")
- elif operation == "remove":
- try:
- index = int(do[1])
- node = a_dllist.get_node(index)
- if node is None:
- print("No such index.")
- continue
- a_dllist.remove(node)
- except:
- print("Invalid input format for remove.")
- elif operation == "quit":
- break
- else:
- print("Unknown operation.")
- opt = input("\nDo you want to try again? (yes/no): ").strip().lower()
- if opt == "no":
- print("Exiting program...")
- break
- elif opt != "yes":
- print("Invalid choice. Exiting program...")
- break
This Python program provides a full implementation of a doubly linked list with interactive operations. It uses `Node` and `DoublyLinkedList` classes to manage the list. Each node contains `data`, a `next` pointer, and a `prev` pointer. The `DoublyLinkedList` class supports insertion at the beginning or end of the list, insertion before or after a specified index, deletion of a node by index, and displaying the current list.
In the interactive main loop, users are presented with a menu where they can choose operations like `insert after
Output:
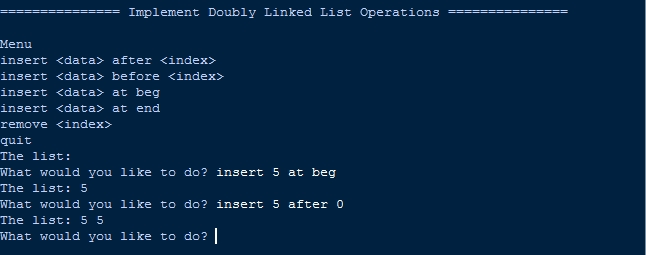
There you have it we successfully created How to Implement Doubly Linked List Operations in Python. I hope that this simple tutorial help you to what you are looking for. For more updates and tutorials just kindly visit this site. Enjoy Coding!
More Tutorials for Python Language

