Print String Permutations in Lexicographic Order Using Recursion in Python
In this tutorial, we will learn how to program "Print String Permutations in Lexicographic Order Using Recursion in Python." The objective is to generate all possible permutations of a given string in lexicographic order using recursion. This tutorial will guide you step by step through the entire process of implementing the recursive logic to achieve this task. By the end of this tutorial, you will have a solid understanding of how to generate string permutations effectively, helping you strengthen your problem-solving abilities and enhance your Python coding skills.
This topic is straightforward to understand. Simply follow the instructions provided, and you will complete it with ease. The program will guide you step by step through the process of computing exponentiation. So, let’s dive into the coding process!
Getting Started:
First you will have to download & install the Python IDLE's, here's the link for the Integrated Development And Learning Environment for Python https://www.python.org/downloads/.
Creating Main Function
This is the main function of the application. The following code will display a simple GUI in terminal console that will display program. To do this, simply copy and paste these blocks of code into the IDLE text editor.- from math import factorial
- def print_permutations_lexicographic_order(s):
- """Print all permutations of string s in lexicographic order."""
- seq = sorted(list(s)) # start with smallest (lexicographic order)
- while True:
- print(''.join(seq))
- if not get_next_permutation(seq):
- break
- def get_next_permutation(seq):
- """Transforms the sequence into the next lexicographic permutation.
- Returns False if there is no next permutation."""
- # Step 1: Find longest non-increasing suffix
- i = len(seq) - 2
- while i >= 0 and seq[i] >= seq[i + 1]:
- i -= 1
- if i == -1:
- return False # no more permutations
- # Step 2: Find successor to pivot
- j = len(seq) - 1
- while seq[j] <= seq[i]:
- j -= 1
- seq[i], seq[j] = seq[j], seq[i]
- # Step 3: Reverse suffix
- seq[i + 1:] = reversed(seq[i + 1:])
- return True
- while True:
- print("\n=============== Print String Permutations in Lexicographic Order ===============\n")
- s = input('Enter the string: ')
- print_permutations_lexicographic_order(s)
- opt = input("\nDo you want to try again? (yes/no): ").strip().lower()
- if opt == 'no':
- print("Exiting program...")
- break
- elif opt != 'yes':
- print("Invalid choice. Exiting program...")
- break
This Python program generates and prints all **permutations of a string in lexicographic order**. It first sorts the characters of the input string to ensure the sequence starts from the smallest lexicographic arrangement. The function `get_next_permutation()` is used to transform the current sequence into the next lexicographic permutation by identifying a pivot point, swapping with the rightmost successor, and reversing the suffix. The main function `print_permutations_lexicographic_order()` keeps printing permutations until no further arrangement is possible. The program runs in a loop where the user inputs a string, all its permutations are displayed, and then the user is prompted whether to try again or exit.
Output:
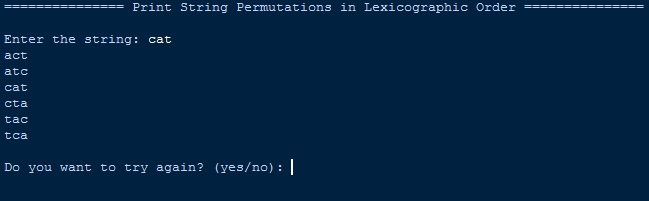
There you have it we successfully created Print String Permutations in Lexicographic Order Using Recursion in Python. I hope that this simple tutorial help you to what you are looking for. For more updates and tutorials just kindly visit this site. Enjoy Coding!
More Tutorials for Python Language

