Simple Calculator using a Class in C#
Submitted by donbermoy on Sunday, July 6, 2014 - 11:41.
In this C# tutorial, I will teach you how to create a program that will compute sum, difference, quotient, and product as just a simple calculator that uses a class.
Now, let's start this tutorial!
1. Let's start with creating a Windows Form Application in C# for this tutorial by following the following steps in Microsoft Visual Studio: Go to File, click New Project, and choose Windows Application.
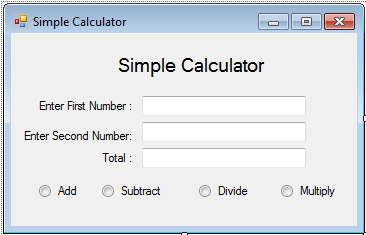
2. Next, add one TextBox named TextBox1 for inputting first number, Textbox2 for inputting second number, and Textbox3 for displaying the total.Insert also 4 RadioButton named Radio_Addition for addition operation, Radio_Subtraction for subtraction operation, Radio_Division for division operation and Radio_Multiplication for multiplication operation. You must design your layout like this:
 3. Create a class named calculate and put this code below.
4. Now, go to your Form and put this code below for the calculator operation.
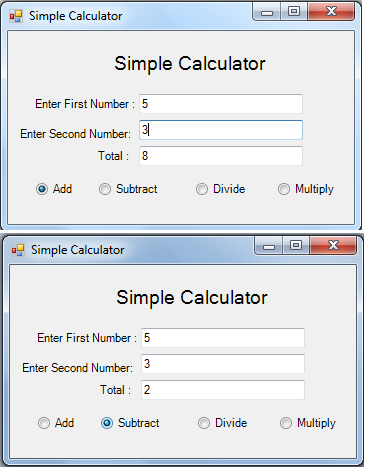
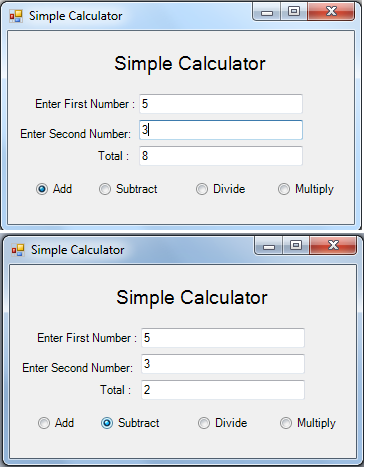
Output:
3. Create a class named calculate and put this code below.
4. Now, go to your Form and put this code below for the calculator operation.
Output:
 For more inquiries and need programmer for your thesis systems in any kind of programming languages, just contact my number below.
Best Regards,
Engr. Lyndon Bermoy
IT Instructor/System Developer/Android Developer/Freelance Programmer
If you have some queries, feel free to contact the number or e-mail below.
Mobile: 09488225971
Landline: 826-9296
E-mail:[email protected]
Add and Follow me on Facebook: https://www.facebook.com/donzzsky
Visit and like my page on Facebook at: https://www.facebook.com/BermzISware
For more inquiries and need programmer for your thesis systems in any kind of programming languages, just contact my number below.
Best Regards,
Engr. Lyndon Bermoy
IT Instructor/System Developer/Android Developer/Freelance Programmer
If you have some queries, feel free to contact the number or e-mail below.
Mobile: 09488225971
Landline: 826-9296
E-mail:[email protected]
Add and Follow me on Facebook: https://www.facebook.com/donzzsky
Visit and like my page on Facebook at: https://www.facebook.com/BermzISware
 3. Create a class named calculate and put this code below.
3. Create a class named calculate and put this code below.
- using System.Diagnostics;
- using System;
- using System.Xml.Linq;
- using System.Windows.Forms;
- using System.Collections;
- using System.Drawing;
- using System.Data;
- using System.Collections.Generic;
- using System.Linq;
- namespace MDAS
- {
- public class calculate
- {
- //declare a private variable as a double
- private double _num1;
- private double _num2;
- private double _total;
- //set a readonly property for the total of the MDAS
- public double total
- {
- get
- {
- return _total; //return the total
- }
- }
- //create a property for a private variable so that you can access it
- public double num1
- {
- get
- {
- return _num1; //return the first value
- }
- set
- {
- _num1 = value; //set the first value
- }
- }
- public double num2
- {
- get
- {
- return _num2;
- }
- set
- {
- _num2 = value;
- }
- }
- //create the sub procedures of the MDAS
- public void multiply()
- {
- //formula of multiplication
- _total = num1 * num2;
- }
- public void divide()
- {
- //formula of division
- _total = num1 / num2;
- }
- public void add()
- {
- //formula of addition
- _total = num1 + num2;
- }
- public void subtract()
- {
- //formula of subtraction
- _total = num1 - num2;
- }
- }
- }
- using System.Diagnostics;
- using System;
- using System.Xml.Linq;
- using System.Windows.Forms;
- using System.Collections;
- using System.Drawing;
- using System.Data;
- using System.Collections.Generic;
- using System.Linq;
- namespace MDAS
- {
- public partial class Form1
- {
- public Form1()
- {
- InitializeComponent();
- }
- //create a sub procedure for the events of clicking the radio button that handles all of it.
- public void RadioButton_Click(object sender, System.EventArgs e)
- {
- //call a constructor method and return to cal as an instance of a class
- //declaring the string variable represent as a textbox
- string txtnum1 = TextBox1.Text;
- string txtnum2 = TextBox2.Text;
- //declaring the double variable
- double dbl_val1 = default(double);
- double dbl_val2 = default(double);
- if (Information.IsNumeric(txtnum1) && Information.IsNumeric(txtnum2)) //check if the textbox has a numeric value
- {
- //convert the string to double
- dbl_val1 = double.Parse(txtnum1);
- dbl_val2 = double.Parse(txtnum2);
- //get the value of the converted variable
- //to pass it into the variable in the class
- cal.num1 = dbl_val1;
- cal.num2 = dbl_val2;
- //the condition is, if the radiobutton is clicked,
- //the operation of MDAS executes.
- {
- //result:
- cal.multiply(); //call a subname in a class for multiplying
- }
- {
- //result:
- cal.divide(); //call a subname in a class for dividing
- }
- {
- //result:
- cal.add(); //call a subname in a class for adding
- }
- {
- //result:
- cal.subtract(); //call a subname in a class for subtracting
- }
- }
- else
- {
- //the result is:
- //if the textbox is empty or has a string value
- TextBox3.Text = "Enter a number";
- return ;
- }
- //put the result of the MDAS to a textbox.
- TextBox3.Text = cal.total.ToString();
- }
- }
- }
 For more inquiries and need programmer for your thesis systems in any kind of programming languages, just contact my number below.
Best Regards,
Engr. Lyndon Bermoy
IT Instructor/System Developer/Android Developer/Freelance Programmer
If you have some queries, feel free to contact the number or e-mail below.
Mobile: 09488225971
Landline: 826-9296
E-mail:[email protected]
Add and Follow me on Facebook: https://www.facebook.com/donzzsky
Visit and like my page on Facebook at: https://www.facebook.com/BermzISware
For more inquiries and need programmer for your thesis systems in any kind of programming languages, just contact my number below.
Best Regards,
Engr. Lyndon Bermoy
IT Instructor/System Developer/Android Developer/Freelance Programmer
If you have some queries, feel free to contact the number or e-mail below.
Mobile: 09488225971
Landline: 826-9296
E-mail:[email protected]
Add and Follow me on Facebook: https://www.facebook.com/donzzsky
Visit and like my page on Facebook at: https://www.facebook.com/BermzISware